Water is one of our limited natural resources that is now under pressure in this new millennium due to overconsumption, pollution and climate change. More than 70% of the Earth is covered by water, yet only 2.5% of this is freshwater and more than 98% of this is locked in ice and not available for us to use. While the total quantity of water on earth is unchanging the availability of freshwater for human use, agriculture, and industry, not to even mention the biosphere’s needs, is becoming scarce and competition for it is fierce. When water has been used it generally cannot be reused unless it undergoes special, and in most instances expensive, treatment.
Water Scarcity is an issue that threatens life itself causing thirst, food shortages displacement and disease. More than 4 billion people worldwide are at risk of drought and half a billion already face severe water scarcity year round. When water is so hard found, even sub prime, or heavily contaminated water, is the only alternative. 2 billion people around the world use contaminated water as their main source of hydration, leading to the proliferation of lethal diseases such as diarrhoea, cholera, dysentery, and typhoid.
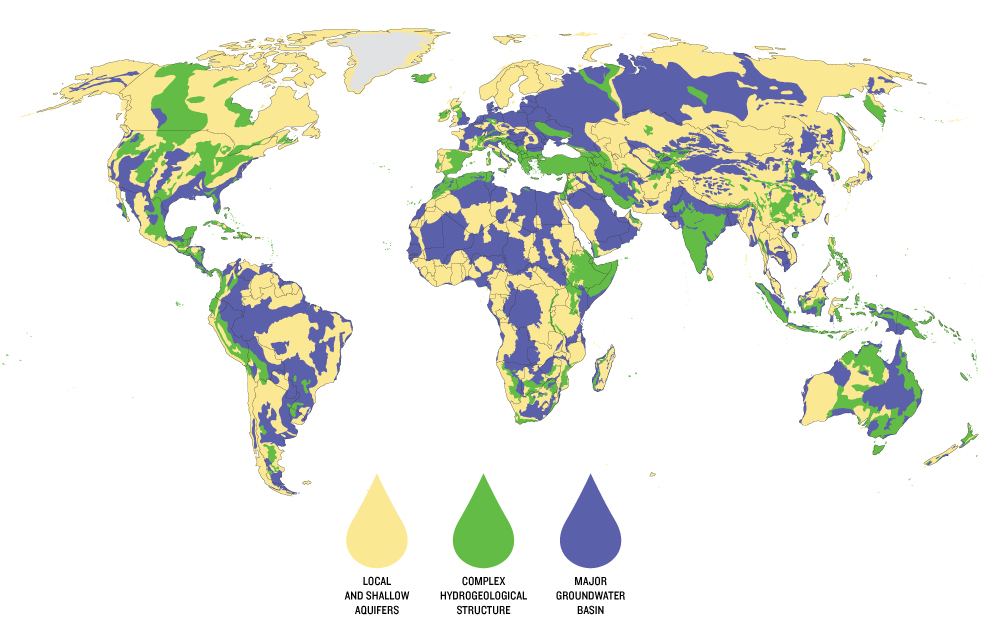
Aquifers and groundwater reservoirs have been an important alternate source of water in drought stricken areas, however 21 of the 37 greatest aquifers in the world have passed their sustainable tipping point. A further 13 have recently been deemed high-risk. Mostly developing countries in Africa and Asia are affected, but developed countries are staring to become affected as well, including in Europe and North America. The Aquifers underneath South East USA, Eastern Europe, Northern India, West Australia, and China are being depleted at alarming rates. The California Valley Aquifer system is already providing 60% of the fresh water needed. If the drought in California continues, the depleted aquifer will be expected to provide virtually all of the water needed this year in the state (even though it is already beyond the point where it can recharge it self). Even more worrisome – the Arabian underground water system, a water source for more than 60 million people, is the most stressed aquifer in the world.

At the other extreme of water disasters, flooding displaced 8.3 million people in 2014 alone. With storms included, the equivalent of 62,000 people have been displaced every day in the last seven years. Because the water cycle is so responsive to changing circumstances, when there is drought in one place, there will be flooding and severe storms in others. Social issues including displacement and conflict are caused directly and indirectly by the disruption of the water cycle, which creates water imbalance.
The water cycle is a natural phenomenon that needs balance to function, a profound paradigm shift is necessary to truly understand the myriad of effects that water overuse, scarcity and cycle disruption can cause in the complex and interconnected world in which we live. Drought in one place means flooding in another, ecological imbalance in the other side of the world means conflict or disease locally. With time as a factor, abusing thousand year old aquifers during long term dry spells will generate a more intrinsic, compounded problem to be solved by the next generation.
Don´t miss next week the steps needed to be taken in order to offer alternatives and options to a more efficient and adequate utilization of this rich but limited resource.